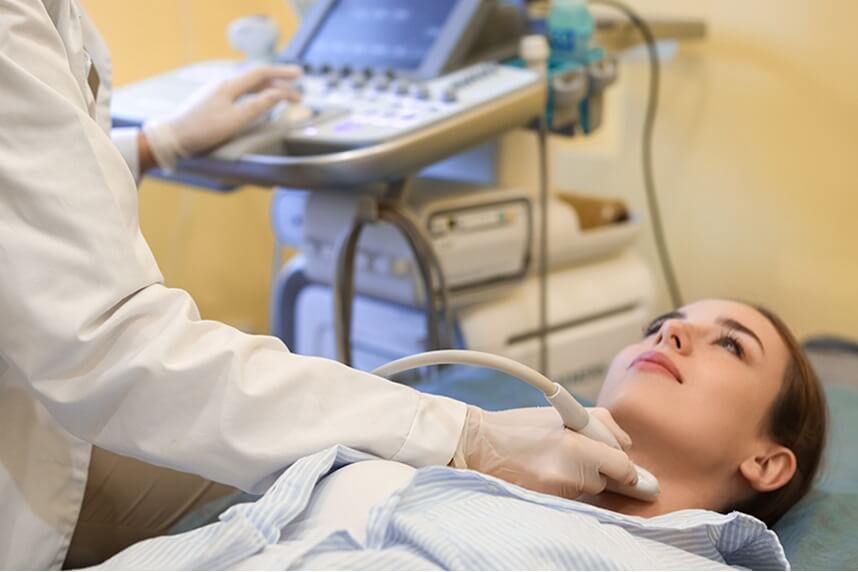
What is a thyroid ultrasound?
Thyroid ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique used to evaluate the thyroid gland and to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. It produces images of the inside of the body using sound waves. It can help assess the size, shape, and texture of the thyroid gland, as well as detect any abnormalities such as nodules, cysts, or inflammation. Thyroid ultrasounds are commonly used to diagnose thyroid disorders, such as thyroid nodules, goiter (swelling of the thyroid gland), thyroiditis, and thyroid neoplasm. In general, thyroid ultrasound for children and adults is similar in terms of the procedure, but interpretation of the results may vary depending on the specific characteristics of each age group.
When is this type of investigation indicated?
Thyroid ultrasound is indicated in several situations:
- thyroid nodules (to determine whether a lump in the neck originates from the thyroid or an adjacent structure, to analyze the appearance of thyroid nodules and determine whether they are benign or have features that require a biopsy);
- guidance for procedures, including needle biopsies (removal of tissue samples for lab tests) or guiding the insertion of a catheter or other drainage device;
- thyroid disorders;
- thyroid neoplasm;
- thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid);
- monitoring the evolution or changes in thyroid nodules or other thyroid conditions over time (checking whether a thyroid nodule has grown significantly over time);
- follow-up – to monitor post-treatment effectiveness for thyroid conditions;
- pregnancy – sometimes, thyroid ultrasound is used during pregnancy to evaluate thyroid nodules or thyroid function, especially if there is concern about the pregnancy being affected by a thyroid condition.
The preparation procedure for a thyroid ultrasound is usually simple:
- clothing – wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes; you may be asked to remove neck jewelry or clothing that interferes with the exam. You may also be asked to change into a special gown provided by the clinic;
- medications – continue taking your medications as prescribed unless your doctor gives you other instructions;
- food – in most cases, there are no restrictions on eating or drinking before a thyroid ultrasound.
The procedure usually takes between 15 and 30 minutes, and afterward you can resume your normal activities. Ultrasounds are very sensitive to movement and, in the case of active or crying children, the process may take longer. Therefore, for a smooth experience, it often helps to explain the procedure to your child in advance. You may also bring books, toys, or music to help distract them.
Benefits of thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound offers several benefits:
- non-invasive (no needles or injections used);
- painless (may be temporarily uncomfortable, but should not be painful);
- widely available, easy to use, and less expensive than most other imaging methods;
- radiation-free (making it extremely safe);
- provides detailed and clear images of the thyroid gland and surrounding structures (soft tissues) that do not appear well on X-rays, allowing accurate diagnosis of thyroid nodules, cysts, goiter, thyroiditis, and thyroid neoplasm;
- early detection – thyroid ultrasound can detect thyroid nodules and other abnormalities at an early stage, often before they are palpable during a physical exam;
- biopsy guidance – since ultrasound provides real-time images, it helps guide fine needle aspiration biopsies and fluid aspiration procedures, allowing for sampling of thyroid nodules for further analysis, which can help diagnose thyroid cancer;
- allows monitoring of the size and characteristics of thyroid nodules over time, helping to assess changes and determine the need for further evaluation or treatment.
Important to know is that thyroid ultrasound poses no risk to the patient and can be safely repeated as often as necessary.
Thyroid Ultrasound Prices
You can find here a detailed list of individual service prices. However, any proper healing process is based on a mixed plan of therapies and procedures, customized according to the condition, stage, patient profile, and other objective medical factors. Therefore, to configure a treatment plan, with the involved therapies, periods, and the corresponding fee, please make an appointment here for an initial consultation.
Centrokinetic is the place where you will find clear answers and solutions for motor function problems. The clinic dedicated to musculoskeletal conditions is divided into the following specialized departments:
- Orthopedics, a department made up of an extremely experienced team of orthopedic doctors specialized in sports trauma.
- Pediatric orthopedics, where sports injuries in children (ligament and meniscus injuries), spinal deformities (scoliosis, kyphosis, hyperlordosis), and foot deformities (hallux valgus, hallux rigidus, clubfoot, flatfoot, cavus foot) are treated.
- Neurology, which has a high-performance department where consultations, electroencephalograms (EEG), and electromyographies (EMG) are performed.
- Medical rehabilitation for adults and children, a department specializing in the recovery of professional athletes, spinal conditions, and the rehabilitation of children with neurological and traumatic conditions. Our experience is extremely extensive, having treated over 5000 professional athletes.
- Medical imaging, the clinic is equipped with ultrasound and MRI, high-performance devices dedicated to musculoskeletal conditions, and complemented by an experienced radiologist: Dr. Cosmin Pantu, specialized in musculoskeletal imaging.
- Rheumatology, a full department that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and recovery of patients with non-surgical locomotor system conditions.
- Vascular surgery, a super-specialized department in diagnosing and treating blood vessel diseases, that is, of arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels.
- Psychology and speech therapy. Neurological or musculoskeletal conditions can have a psychological impact on the patient, which is why we believe complete healing involves focusing not only on the musculoskeletal issue but also on the psychological consequences.
- Neurofeedback. This revolutionary method helps you improve your concentration, reduce anxiety, and achieve emotional balance, all through a simple and interactive process.
Stay updated by following Centrokinetic's Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube accounts.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT

































































































































