See details
READ MORE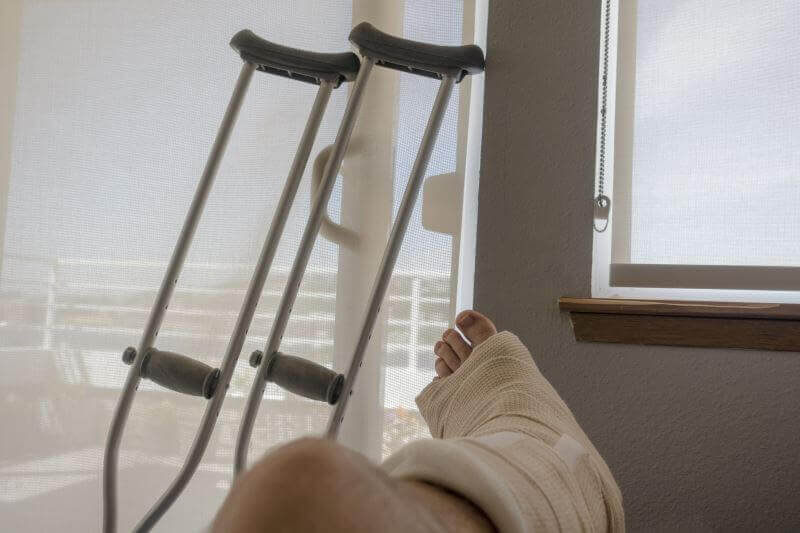
Recovery protocol in the operated metatarsal V fracture
The forefoot bones play an important role in normal walking. Studies have shown that the two sesamoid bones and the head of the 2-5 metatarsals share body weight evenly while walking.General principles
- The patient will use the crutches, without stepping on the operated leg, until the edema is in remission
- Postoperatively, the patient will have his foot immobilized in a walker for 1-2 weeks
- Avoid walking or standing for long periods in the first week to control local edema and pain.
- Apply ice 3-5 times a day (15 minutes each time) to control edema and the inflammatory process
- Raise the operated leg above the level of the heart to limit edema and the inflammatory process
- No impact exercises in the first 6 weeks post-surgery

Causes
The mechanism of production is usually a sports injury or car accident. Fractures are divided according to location into metatarsal base fractures and distal spiral fractures (dancer's fracture). In addition, the basic metatarsal fractures are divided into 3 areas.Zone 1 fractures can be treated orthopedically and symptomatically. Symptoms may persist for up to 6-8 weeks. Zone 2 fractures can be treated orthopedically by plastering and walking with partial or surgical support. Studies have shown that orthopedic treatment for 8-10 weeks is ideal. Zone 3 fractures require more aggressive treatment, which consists of surgery and internal fixation with a screw.
Rehabilitation protocol
Week 1
Week 2 - 6
- Start stepping on the operated limb, under the close supervision of the physical therapist, depending on the pain and local edema.
- Radiological examination at 4-6 weeks to monitor healing
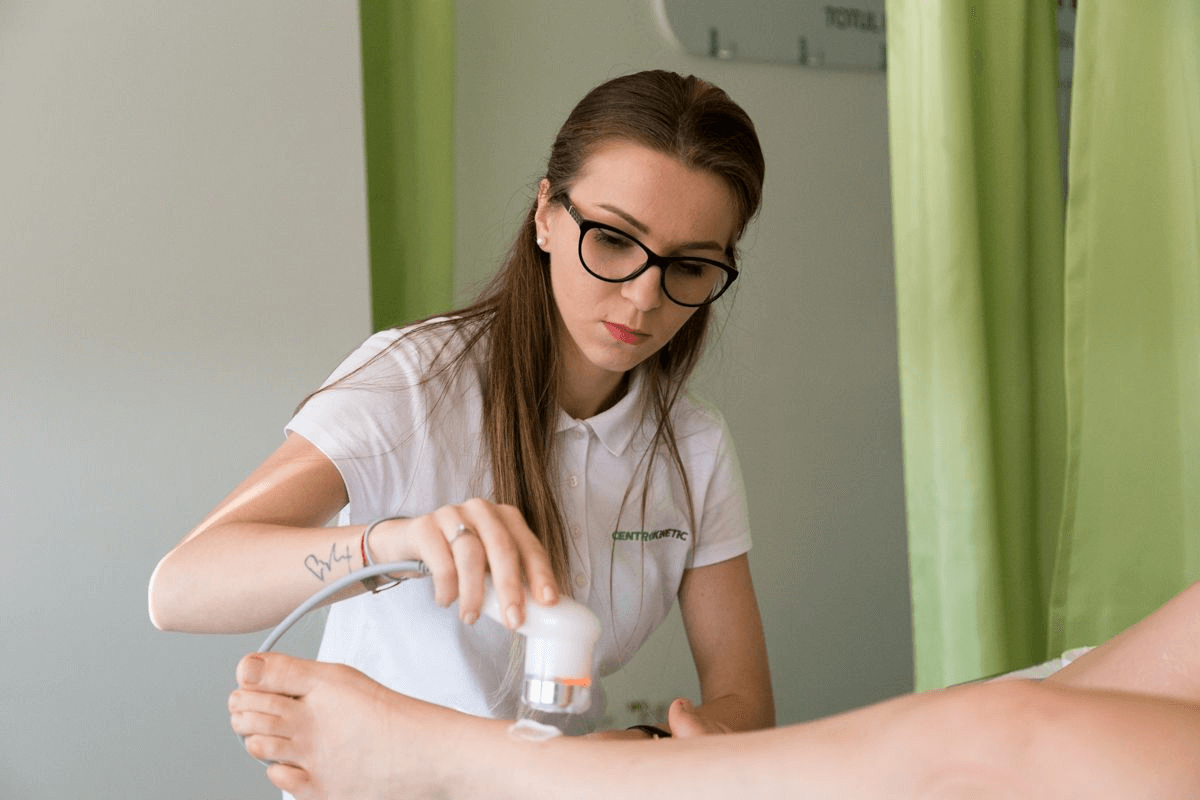
- Soft tissue treatments for local edema prevention, mobility, and soft tissue healing
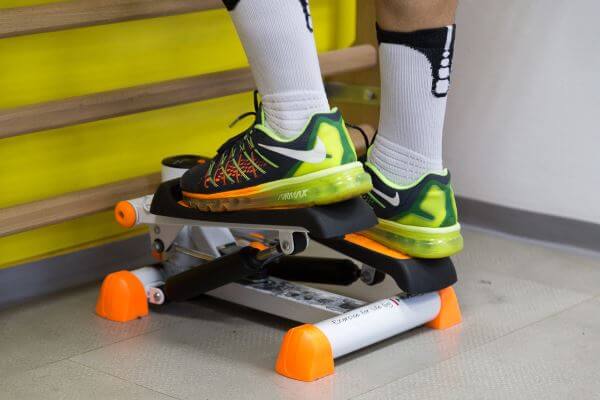
- Cycling, balance exercises
- Stretching in the ankle and foot area and exercises with the help of Theraband bands to regain complete mobility of the foot, as well as to strengthen it
- Progress the functional loading exercises and activities on the operated leg. Avoid jumps and quick changes in direction.
- Continue mobilizing your ankle and foot joints
- Start the exercises specific to the sport you practice
- Increase the level of strengthening, balance, and coordination training for a gradual return to the specific activities of the sport practiced
- Returning to sports activities depends on a complete functional evaluation, specific to your sport, performed by the physical therapist.
SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT