See details
READ MORE
Achilles tendon suture recovery protocol
The origin of the gastrocnemius muscle is in the upper part of the lateral femoral condyle and on the medial condyle of the femur. The insertion is made with the help of the Achilles tendon on the posteromedial surface of the calcaneus. Its most important roles are plantar flexion and knee flexion.General principles
- Avoid forced, both passive and active mobilization of the Achilles tendon for 10-12 weeks
- Carefully monitor the tendon to assess its mobility and the postoperative incision to follow the physiological granulation process. Perform soft tissue treatments (wound mobilization and massage) to prevent local edema and fibrosis.
- All exercises should be closely monitored for any signs of compensation
- No running exercises or jumping in the first 6 months
- Aerobic and general conditioning exercises throughout the recovery process
Causes
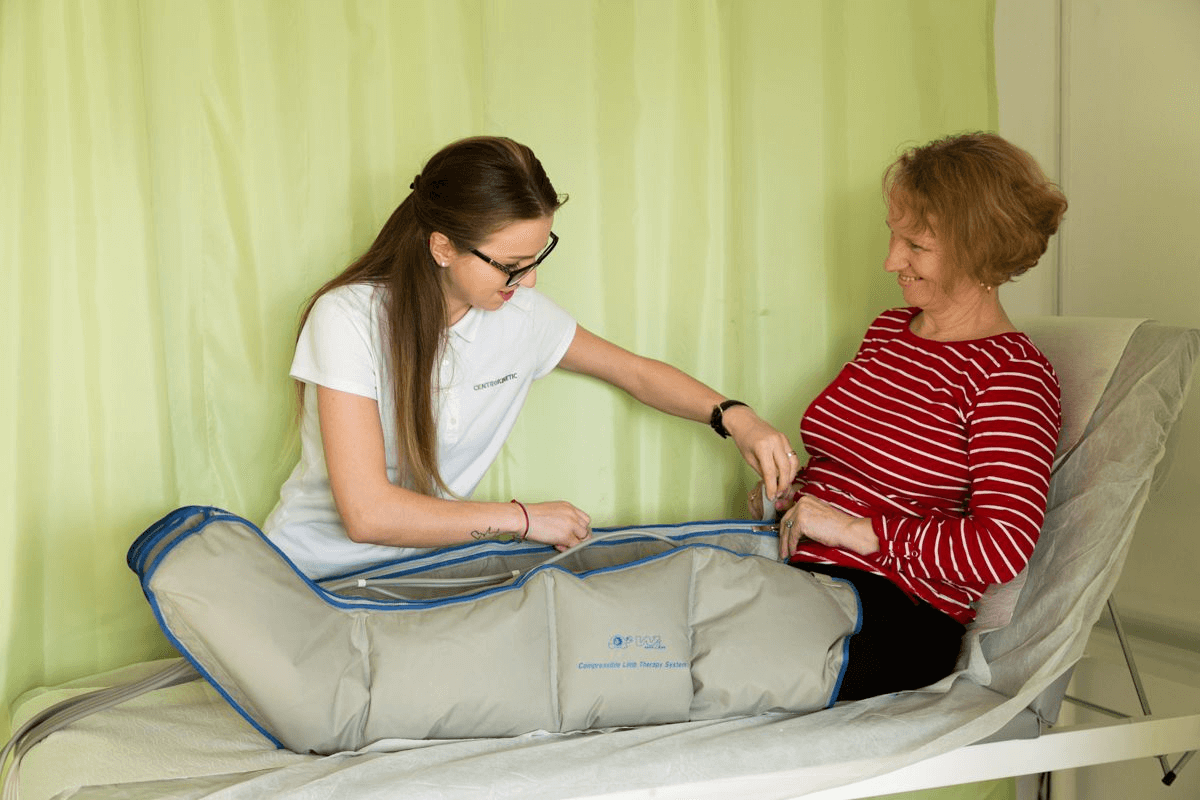

Treatment
It has been and still is quite controversial, many authors compare the results obtained with orthopedic treatment with the surgical one. Interestingly, the results obtained with orthopedic treatment are similar to those obtained with surgical treatment, in the case of an incomplete rupture. In the case of surgical treatment, the recurrence rate is much lower. However, surgery is recommended as the main method of treatment.Rehabilitation protocol
Week 0 - 3- Immobilization in a splint with the foot at 30 degrees plantar flexion
- Do not load on the operated limb in the first 3 weeks
- Control of local pain and edema (cryotherapy, electrical stimulation, soft tissue treatments)
- Soft tissue mobilization to monitor local edema
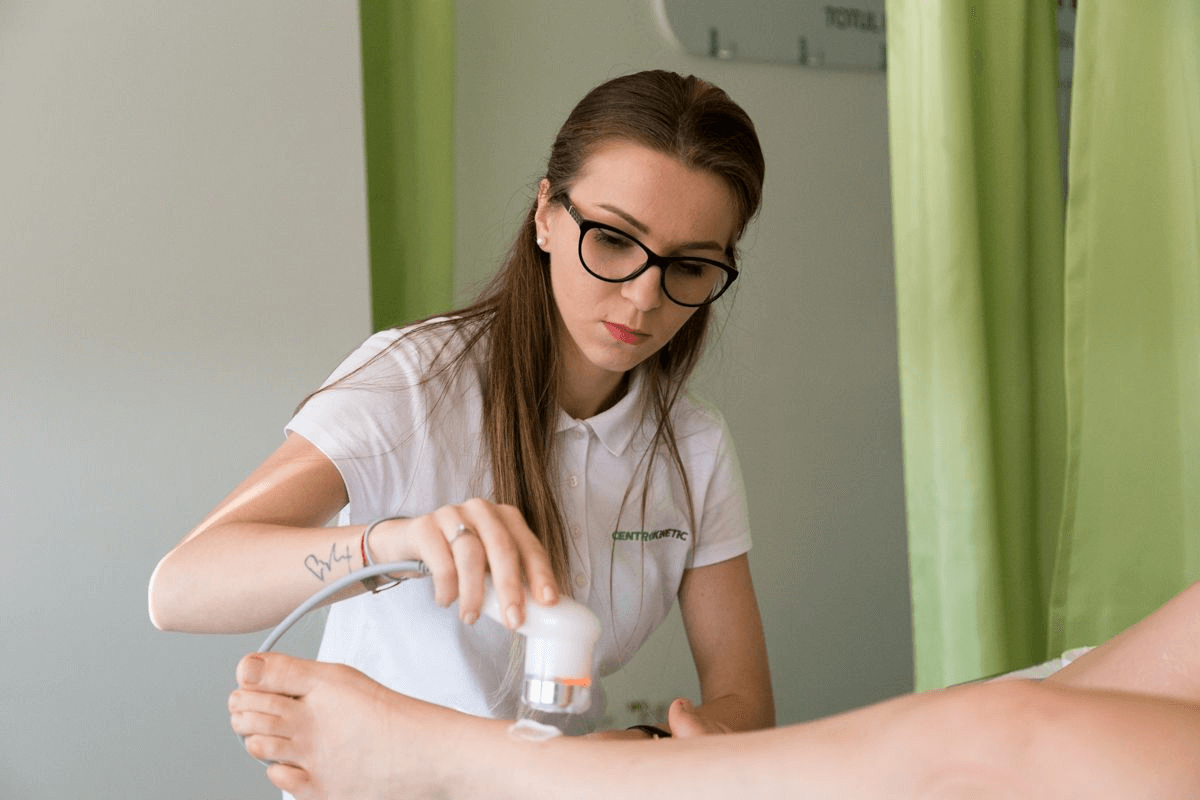

Exercises
- Active movements of the toes, light movements of the foot in the splint, lifting of the operated limb with the knee in extension, flexion/extension of the knee
- Cycling (using only the healthy foot), swimming for cardiovascular exercises
- Minimizing local pain and edema. Walking with crutches, without stepping on the operated limb
- Immobilization in a splint / walking orthosis set at 30 degrees plantar flexion at 3 weeks; adjust 10 degrees each week
- Gradually increase the load from the simple touch of the fingers, for balance, to the contact of the heel with the ground (partial load)
- At 6 weeks, full loading on the operated leg is allowed
- Soft tissue mobilization to monitor local edema
- Initiate passive movements of the foot with dorsiflexion (without exceeding the neutral position), inversion/eversion exercises of the foot depending on the pain tolerance
- At 4 weeks, it is allowed to mobilize the post-operative wound, once it has closed completely
Exercises
- Exercises for lifting the operated limb, with the knee in extension, abduction exercises for the hip, exercises for extending the torso to the bridge position with the limbs in extension
- Isometric exercises of the muscles not involved in the Achilles tendon
- Active movements of the foot with dorsiflexion (light stretching of the Achilles tendon is allowed at 4 weeks)
- Isometric exercises of the Achilles tendon
- Progress the Achilles tendon stretching exercises at 6 weeks
- Proprioceptive exercises, intrinsic strengthening of muscles
- At 6 weeks, you can ride a bike, pushing the pedal only with the heel
- Neutral foot position
- No crutches and full charging at 6 weeks postoperatively
Week 8 - 12
- After 8 weeks, you can wear regular shoes, but that includes plantar lifts.
- Full load on the operated limb, walking exercises
- Start and gradually increase active and resistance exercises of the Achilles tendon (submaximal isometric exercises, isotonic exercises, Theraband exercises)
- Cycling, swimming
- Full range of ankle movement
- Tolerance of using ordinary footwear, normal walking, without compensation
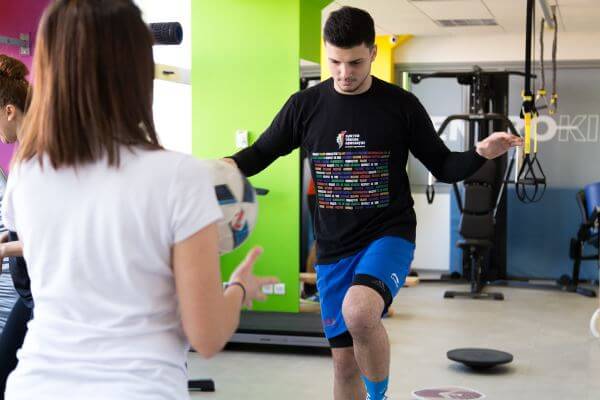

Month 3 - 6
- Squatting exercises (under the close monitoring of the physical therapist), lifting exercises on the fingertips (bilateral - progressing unilaterally), diving exercises
- Medicinal bicycle, elliptical bicycle, rowing machine
- If you do not have excessive fibrosis, you can continue recovery exercises at home
- You can start light running exercises, jumping exercises, excentric loading exercises, light exercises, specific to the sport practiced
- After a careful evaluation by the physical therapist, you can return to the sport you practice.

SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT