Vezi detalii
CITESTE MAI MULTActualizat: 16-01-2024 / Publicat: 25-01-2017
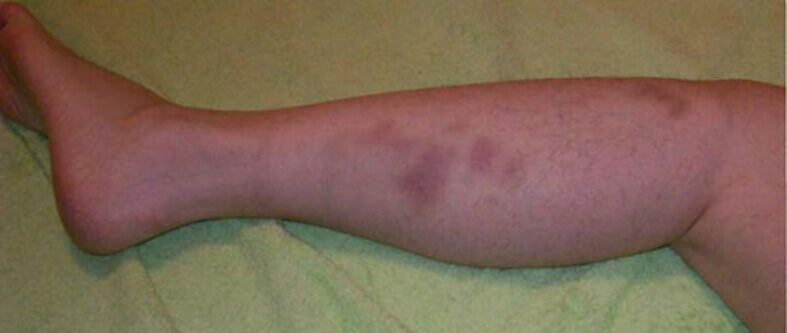
Physiotherapy after contusions
Bruises are common as a result of direct trauma from falling, crushing, or hitting a blunt body. If the force of traumatic action is exerted obliquely, tangentially, the soft tissue injury will be more extensive but easier, but if it acts perpendicularly, the injury will be deeper, more serious and localized.

The general recommendation is to avoid heat for the first 24-48 hours so as to avoid the spread of hematoma and local edema. Patients who have suffered concussions of the thighs are recommended to use crutches during mobilization because these contusions can be very painful, the load on the bruised limb can extend the injuries caused by the contusion.
The knee articulation should be flexed to the level of pain tolerance, in tandem with compression, thus facilitating drainage of edema from the region.
The contusion normally stabilizes in the first 24-48 hours, a secondary assessment dictating the treatment to be performed and the prognosis. Surgery is not necessary in case of contusions except in situations where compartment syndrome is confirmed.
In the second phase, also known as the recovery / regeneration phase, the main goal is to restore mobility and regain full range of motion. Early mobilization has been shown to significantly reduce recovery time and increase muscle breaking strength.
The patient is ready to progress to the next level of the recovery program when the full range of motion has been restored. Jackson and Feagin have shown that the patient is ready to advance to the next level when a 90-degree knee flexion is achieved. Isometric exercises are started to limit the pain. The load on the bruised limb will be done until the pain threshold. Also, early mobilization increases the vascularity of the injured area, thus decreasing the healing period.
RECUPERARI DE SUCCES
PROGRAMEAZA-TE
LA O CONSULTATIE
Vezi aici modalitatile de programare si localizarea clinicii
PROGRAMARE