See details
READ MORE 
Discover the hyperbaric medicine center opened in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest, with multiple medical and anti-aging uses. The Baroks chamber has 5 seats, and operates at a constant pressure of 2.5 atmospheres, being fully automated and having protocols for each condition, and can be used individually for each patient.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy - benefits
Patients who use the clinic's hyperbaric therapy services benefit from:
- The only medically accredited hyperbaric therapy chamber in Bucharest, which operates at 2.5 atmospheres (those for aesthetic use go to 1 atmosphere and have no medical benefits).
- A safe medical procedure, without irradiation, without pain, without other side effects.
- The specialized medical team consists of recovery doctors, orthopedists, rheumatologists, neurologists, and neurosurgeons, meaning a multidisciplinary team specialized in all diseases that can be treated with hyperbaric therapy.
- Premium conditions at a fair price. Our clinic is recognized for the conditions offered and for the care of each patient. But we do not need to pay exorbitant prices to have access to quality medical services. At Centrokinetic you can find an affordable and fair price. But note that we do not have a contract with the National Health Insurance House (we do not offer state reimbursed services)
Centrokinetic is keeping contact with prestigious clinics and universities in Belgium, the Netherlands, France, and Greece to constantly update treatments to provide patients with the best medical solutions.
Introduction
Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is a well-recognized phenomenon that may follow virtually any ischemic episode to tissues from interrupted blood flow, including direct traumatic tissue injuries, pressure-induced injuries, and cold injuries or burns, embolic, thrombotic, or localized inflammatory occlusion insults. It is also described following vascular or cardiovascular reperfusion procedures and post compartment syndrome fasciotomies.
Tissue injury and/or death from this initial ischemic insult is determined by a combination of degree and duration of the occlusion and extent and type of tissue involved by the affected watershed area of capillary or arteriolar distribution. When circulation is restored, the occlusion is relieved, or the vessel is re-cannulated, a recurrent ischemic effect may occur within the following 4 to 8 hours, and cell death can continue for up to 3 days after the reperfusion. The release of endothelial chemotactic substances initiated by the original injury or insult creates an intravascular inflammatory response.
This inflammatory response is at least partially responsible for further vascular occlusion of downstream tissues from edema. It is worsened by additional release from the second round of reactive oxygen species generated by the freshly oxygenated blood in an affected region depleted of protective free radical scavengers responding to the initial insult.
If initiated early, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been found to ameliorate the damaging effects of reperfusion by early modulation of inflammation, maintenance of metabolic function in downstream tissues, and reintroduction of oxidation scavengers.
.jpg) | .jpg) |
Function
The initial microvascular injury may be caused indirectly by upstream vascular occlusion or directly from a traumatic crush injury. Either mechanism results in varying degrees of endothelial insult. The initial ischemia triggers hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) that stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) release, associated with the enhanced permeability of capillaries and arterioles. Neutrophil aggregation and adhesion to sensitized endothelial cells result in further cellular permeability and the relaxation of the cell-to-cell junctions (diapedesis).
The increased permeability leads to a greater diffusion of fluid across the tissues (edema) and extracellular extravasation of leukocytes. This leukocyte activation is part of the inflammatory response, concentrating and utilizing reactive oxygen species for the phagocytic process of killing bacteria. Ischemic hypoxia drives the affected tissue into anaerobic metabolism, resulting in adenosine 5´ triphosphate depletion and decreased intracellular pH with lactic acid accumulation.
Further ischemic injury may occur at the cellular level when calcium ion efflux occurs from inactivated adenosine triphosphatases, accompanied by the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, further impairing adenosine 5' triphosphate production. Other biochemical events occur that don’t directly relate to tissue injury, but when fueled by the reintroduction of oxygen when circulation is restored, trigger a cascade event of elements that exacerbates further injury and sometimes full end-organ failure in downstream flow.
Following reperfusion, the endothelial cells in their activated state produce more reactive oxygen species but less nitric oxide, a highly effective regulator of vascular tone, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. The mechanisms leading to reperfusion injury are complex and still not fully understood but are likely related to a combination of factors, including:
- The rapid reintroduction of oxygen increases reactive oxygen species such as the potent superoxide anion and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and reactive nitric oxide species (RNOS), overwhelming the already depleted source of antioxidant catalases.
- Intracellular calcium overload with the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore leads to mitochondrial swelling and apoptosis.
- Endothelial dysfunction with a pronounced inflammatory reaction occurs.
Precautions
Hyperbaric oxygen promotes the VEGF-induced enhancement of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. In addition to the scavenger effect of this antioxidant, this catalase may affect the mitogenic and anti-apoptotic actions of VEGF in preserving the integrity of the endothelium, thereby improving blood supply to the ischemic tissues. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can reduce leukocyte adherence on the endothelium of venules and block the progressive arteriolar vasoconstriction associated with reperfusion injury.
Fragile tissues may have a greater risk of a total loss of function due to cellular apoptosis following the second hypoxic insult presented by the Ischemia-Reperfusion injury. These tissues include nervous tissue, lung parenchyma, or any other previously damaged connective tissue.
What are the effects of oxygen therapy on the body?
- Decreases inflammation
- Increases the body's oxygen saturation by 20-30%
- Increases the body's immunity
- Increases blood circulation and stimulates the formation of new capillaries
- Decreases toxins in the body
- Stimulates the production of new blood cells
- Increases healing rate
.jpg) | 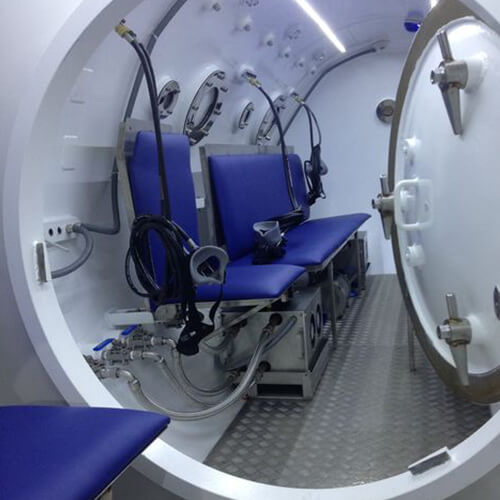 |
Clinical significance
Most nontraumatic ischemic events are related to vascular occlusion from atherosclerosis or other thromboembolic diseases. This risk is usually from hereditary factors that, along with advanced age and gender, cannot be controlled by preventive measures. Many associated risk factors can be controlled, often with the management of a primary care provider. Diet, activity, alteration of nutritional balance for weight loss as needed, and moderation of alcohol intake may help mitigate some additional risk. Medication may be appropriate to help diabetic patients maintain good glycemic control.
Iatrogenic causes can also contribute to ischemic tissue occlusive events, including postoperative reactive inflammatory responses or sudden hypotensive responses to medical management. Air-gas embolisms can arise from insufflation during endoscopic procedures or delivery of anesthetic gases due to over-pressurization of poorly compliant lungs. Any of these actions may be enough to cause a vaso-occlusive occurrence.
Additional endothelial damage may occur with the complete occlusion of flow, thereby inhibiting oxygen delivery in any concentration to the affected tissue. Early intervention with oxygenated hemoglobin may mitigate some of this risk by activation and increased production of protective antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, heme oxygenase-1, nitric oxide synthase, and heat shock proteins.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a relatively safe treatment with a primary risk (greater than 1%) of barotrauma to the middle ear and sinus cavities. The only direct contraindication for treatment is the presence of a pneumothorax. The risk for treatment-induced pneumothorax, however, is less than 0.01%. The potential benefits of hyperbaric oxygen therapy outweigh the risks.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513221/
IN CASE YOU HAVEN'T ALREADY HEARD ABOUT US
Centrokinetic is the place where you will find clear answers and solutions for your motricity problems. The clinic is dedicated to osteoarticular diseases and is divided into the following specialized departments:
- Orthopedics , a department composed of an extremely experienced team of orthopedic doctors, led by Dr. Andrei Ioan Bogdan, primary care physician in orthopedics-traumatology, with surgical activity at Medlife Orthopedic Hospital, specialized in sports traumatology and ankle and foot surgery. .
- Pediatric orthopedics , where children's sports conditions are treated (ligament and meniscus injuries), spinal deformities (scoliosis, kyphosis, hyperlordosis) and those of the feet (hallux valgus, hallux rigidus, equine larynx, flat valgus, hollow foot).
- Neurology , which has an ultra-performing department, where consultations, electroencephalograms (EEG) and electromyography (EMG) are performed.
- Medical recovery for adults and children , department specialized in the recovery of performance athletes, in spinal disorders, in the recovery of children with neurological and traumatic diseases. Our experience is extremely rich, treating over 5000 performance athletes.
- Medical imaging , the clinic being equipped with ultrasound and MRI, high-performance devices dedicated to musculoskeletal disorders, and complemented by an experienced team of radiologists: Dr. Sorin Ghiea and Dr. Cosmin Pantu, specialized in musculoskeletal imaging.
Find the latest news by following the Facebook and YouTube accounts of the Centrokinetic clinic.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in intestinal pneumatosis
Cystoid or cystic intestinal pneumatosis (intestinal emphysema) is a symptom that can occur in many gastrointestinal diseases. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be a successful treatment of cystoid intestinal pneumatosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in cell damage caused by radiation in gynecological cancers
Gynecological cancers treated with a combination of external beam radiation and brachytherapy, especially cervical and vaginal cancers, can result in the apex of the vagina receiving a high dose of radiation. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has positive effects on the radiated tissues, especially the head, neck, anus, and rectum.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in post-radiotherapy CNS injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves the use of so-called levels of oxygen under pressure to increase the level of oxygen in the blood. The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves oxygen treatment for soft tissue radionecrosis. Read this article and find out more.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygenation vs normobaric oxygenation in CO poisoning
Prolonged CO exposure is responsible for more than half of fatal poisonings and is also one of the leading causes of poisoning in Western countries. We aimed to compare the effectiveness of therapy with hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) versus normobaric oxygen (NBO) in the setting of carbon monoxide poisoning (COP).
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in diabetic foot
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be effective for Wagner's grade 3 and 4 diabetic foot ulcers and need to study the real problems with patients seeking treatment and demonstrates the need to study the real problems with patients seeking treatment. The results show that it is important to follow the treatment in order for the HBOT to be efficient.
READ MOREThe role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in sports medicine
Hyperbaric oxygen is used in sports medicine to reduce hypoxia and edema and is also effective in treating stroke injuries and acute traumatic peripheral ischemia. When used clinically, hyperbaric oxygen should be considered as an adjuvant therapy used as early as possible after the diagnosis of the lesions.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in muscle injuries
Muscle stretches are the most common muscle injuries suffered during performance sports. Rapid recovery from muscle injury is crucial for elite athletes who regularly are exposed to training and increased competition. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a safe and effective method, being a non-invasive treatment
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in sports injuries
Hyperbaric therapies are methods used to treat disease or injury using pressures higher than the local atmospheric pressure inside a hyperbaric chamber. The long-term effects are neovascularization (angiogenesis in hypoxic soft tissues), osteoneogenesis, and stimulation of collagen production by fibroblasts. This is beneficial for wound healing and recovery after irradiation.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in proctitis generated by radiation
Proctitis is the inflammation of the rectal mucosa causing pain, discharge, and other unusual symptoms. Pain can occur during bowel movements, it can be acute or chronic. Symptoms may vary, but the most common is tenesmus (the feeling of needing to go to the toilet), a sensation that persists even after using the toilet. This treatment should be offered to patients who fail to recover with conventional treatments for radiation-induced proctitis.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in refractory osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone or marrow caused by bacteria or mycobacteria. Hyperbaric oxygen treatments can be considered an American Heart Association (AHA) Class II recommendation for the treatment of chronic, refractory osteomyelitis
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in tinnitus
Hyperbaric oxygenation allows a controlled increase in oxygen pressure in the blood. This technique can be used in cases of tinnitus and sudden deafness, when certain changes in the inner ear and brain generate a lack of oxygen and, therefore, a limited intake of energy.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy of ischemia and reperfusion injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been found to ameliorate the damaging effects of reperfusion by early modulation of inflammation, maintenance of metabolic function in downstream tissues, and reintroduction of oxidation scavengers.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in the treatment of second degree burns
HBOT has a beneficial effect on burn wound healing by reducing edema and ensuring there is adequate oxygen in microcirculation. It may speed up epithelialization and suppress unnecessary inflammation that could negatively affect normal wound healing. With further research, HBOT may become an adjuvant therapy to surgery.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric therapy is a form of medical treatment that involves exposing the body to pure oxygen at a higher pressure than normal. There are about 45 diseases approved worldwide to be treated with hyperbaric oxygen.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in the management of patients with malignant otitis externa
Malignant otitis externa is a rapidly spreading bacterial infection that is aggressive and may be fatal if left untreated. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment in which the entire body is placed in an airtight chamber at increased atmospheric pressure and has been proven to be effective for several different medical conditions.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute myocardial infarction
If left untreated, MI will lead to the progressive loss of viable cardiomyocytes, impaired heart function, and congestive heart failure. Oxygen cycling therapy serves as a very attractive option for the treatment of myocardial infarction, because it offers some of the greatest benefits while reducing treatment time and inconvenience to the subject.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen in ischemic ulcers
The present study has demonstrated that adjunct HBOT enhances the reduction of ulcer area and depth at 4 weeks in T2DM patients with ischaemic DFUs. HBOT is known to ensure hyperoxygenation of ischaemic tissue and restoration from hypoxia. Discover the hyperbaric medicine center open in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in femoral condylar osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis of the knee (ONK) is a form of aseptic necrosis resulting from ischemia to subchondral bone tissue. Typically, treatment is invasive. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may provide a noninvasive alternative by improving oxygenation and reperfusion of ischemic areas. This study evaluates the efficacy of HBOT in a series of ONK patients.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in femoral head necrosis
Femoral head necrosis (FHN), also called avascular necrosis, or femoral head osteonecrosis is a common multifactorial condition that affects patients of any age and can lead to substantial clinical morbidity. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) is one of the proposed treatments. Indeed, tissue oxygen promotes angiogenesis that reduces edema. Read about the effectiveness of this treatment.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a devastating and common eye condition. It presents a sudden, unilateral, and painless loss of vision. Even when treated promptly, an acute obstruction of the central retinal artery usually leads to severe and permanent loss of vision.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in irradiated maxillofacial dental implant
There are numerous studies reported for the effectiveness of HBO in the treatment of osteoradionecrosis of various bone tissues. In addition to its usefulness in treating osteoradionecrosis, this therapy can prevent it. It also combats the negative effect of irradiation, stimulates osseointegration, and improves the survival rate of the implant.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in hear loss
The auditory function in the inner ear is maintained by the cochlea, which is known to have a high oxygen demand. Hyperbaric oxygen can increase the tension of oxygen in the perilymph and restore hearing in a significant number of patients with sudden hearing loss. Patients can be treated in a single-seater hyperbaric chamber or in a multiplace chamber.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in traumatic ischemia
Limb trauma, which leads to direct tissue damage, plus local hypoxic disorders caused by the resulting edema, causes acute peripheral ischemia. Surgical treatment and hyperbaric oxygen are not concurrent treatment modalities but are best used to complement each other in order to provide the best outcome for the patient.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in venous embolism
Small gas embolisms, as in this case, present serious risks, especially the complication of cerebral air embolism. To prevent neurological complications, it is necessary to urgently remove the air bubble. HBOT reduces the volume of the bubble, helps eliminate nitrogen, and improves the oxygenation of potentially hypoxic tissue. See the results of hyperbaric therapy in venous embolism.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in osteoradionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a common consequence of radiation provided to cancer patients. Currently, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has a major role in improving wound healing in patients with ORN.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in soft tissue radionecrosis
Discover the hyperbaric medicine center open in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest, with multiple medical and anti-aging uses. The Baroks chamber has 5 seats, and operates at a constant pressure of 2.5 atmospheres, being fully automated and having protocols for each condition, and can be used individually for each patient.
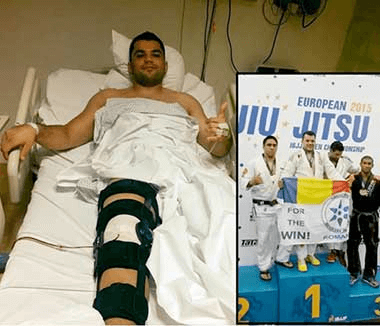
READ MORESUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT