See details
READ MORE.jpg)
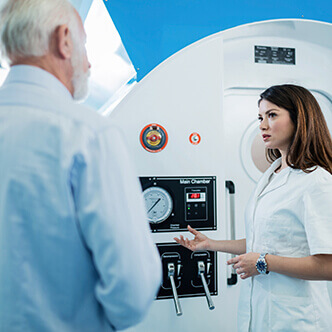
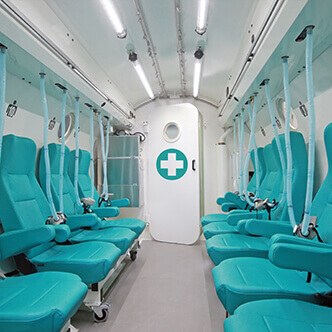
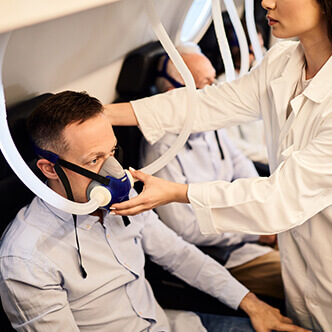
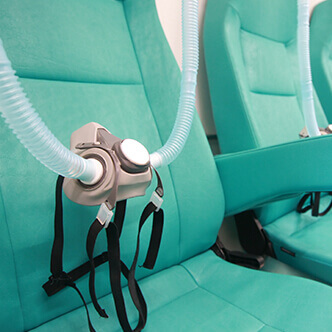
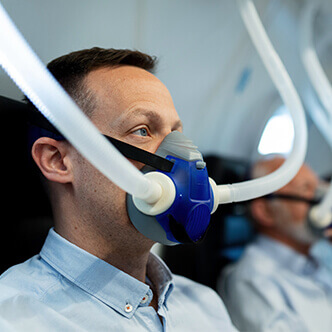
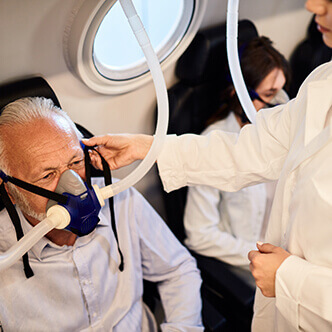
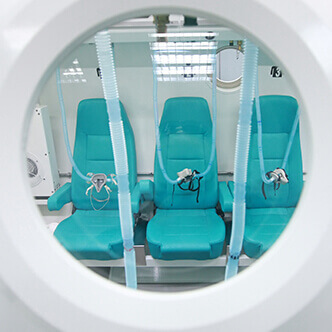
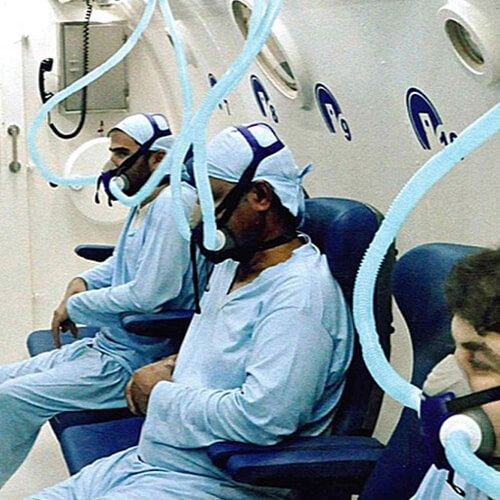
Discover the hyperbaric medicine center opened in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest, with multiple medical and anti-aging uses. The Baroks chamber has 5 seats, and operates at a constant pressure of 2.5 atmospheres, being fully automated and having protocols for each condition, and can be used individually for each patient.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy - benefits
Patients who use the clinic's hyperbaric therapy services benefit from:
- The only medically accredited hyperbaric therapy chamber in Bucharest, which operates at 2.5 atmospheres (those for aesthetic use go to 1 atmosphere and have no medical benefits).
- A safe medical procedure, without irradiation, without pain, without other side effects.
- The specialized medical team consists of recovery doctors, orthopedists, rheumatologists, neurologists, and neurosurgeons, meaning a multidisciplinary team specialized in all diseases that can be treated with hyperbaric therapy.
- Premium conditions at a fair price. Our clinic is recognized for the conditions offered and for the care of each patient. But we do not need to pay exorbitant prices to have access to quality medical services. At Centrokinetic you can find an affordable and fair price. But note that we do not have a contract with the National Health Insurance House (we do not offer state reimbursed services)
Centrokinetic is keeping contact with prestigious clinics and universities in Belgium, the Netherlands, France, and Greece to constantly update treatments to provide patients with the best medical solutions.
 |  |
What is malignant otitis externa?
Malignant external otitis is a rapidly spreading bacterial infection that is aggressive and may be fatal if left untreated. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment in which the entire body is placed in an airtight chamber at increased atmospheric pressure and has been proven to be effective for several different medical conditions.
This study aimed to assess the usefulness of HBOT as an adjunctive treatment in patients with malignant otitis externa. Forty-three diabetic patients, who had malignant otitis externa, underwent control of diabetes mellitus and were treated with ciprofloxacin. HBOT was administered to 15 patients as an adjunctive treatment. All the patients were evaluated clinically (in terms of ear discharge, granulations, and pain severity) and radiologically by a temporal bone computed tomography scan. The minimum follow-up duration in both groups was 2 months. HBOT was administered in one session every other day for 2 months, resulting in a total of 30 sessions. Patient factors analyzed included age, sex, ear discharge, and pain severity.
The addition of HBOT to medical treatment is highly effective and has facilitated considerable improvement in patients.
Introduction
Malignant external otitis is an infection that affects the external auditory canal and temporal bone. The causative organism is usually Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the disease commonly manifests in elderly patients (pts) with diabetes. The infection begins as external otitis that progresses to osteomyelitis of the temporal bone.
The spread of the disease outside the external auditory canal occurs through the fissures of Santorini and the osseocartilaginous junction. Malignant external otitis is a rapidly spreading bacterial infection that accounts for a relatively small proportion of infections, but arises aggressively and may be fatal if left untreated. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment in which the entire body is placed in an airtight chamber at increased atmospheric pressure. In this chamber, the patient is surrounded by and breathes 100% pure oxygen.
This treatment has been proven effective for several different medical and surgical conditions either as a primary or as an adjunctive treatment. The pressure can be increased to as much as three times the normal atmospheric pressure (although the usual treatment pressure is 1.5–2.0 atmospheric depending on the diagnosis). Pure, 100% oxygen is continuously maintained and circulated throughout the chamber during the treatment. HBOT is an effective treatment for acute and chronic damaged tissue of all types – any cause, any duration, any location. The underlying causes can be trauma, infection, autoimmunity, ischemia, hypoxia, toxins, or something similar.
These infections may be single aerobic or anaerobic but are more often mixed infections. They are often observed in compromised hosts who have diabetes or a vasculopathy of another type. These infections are named based on their clinical presentation and include malignant external otitis. Irrespective of the depth of the tissue invasion, these infections have similar pathophysiology that includes local tissue hypoxia, which is exacerbated by a secondary occlusive endarteritis. Multiple clinical studies suggest that HBOT is efficacious in the treatment of necrotizing soft tissue infections. These include case series, retrospective and prospective studies, and nonrandomized clinical trials.
They suggest significant reductions in mortality and morbidity. It is also used to treat many other medical conditions that are still considered experimental by the mainstream medical establishment – despite decades of reported benefits. This article aims to assess the value of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) as an adjunctive treatment of malignant external otitis along with antimicrobial agents.
What are the effects of oxygen therapy on the body?
- Decreases inflammation
- Increases the body's oxygen saturation by 20-30%
- Increases the body's immunity
- Increases blood circulation and stimulates the formation of new capillaries
- Decreases toxins in the body
- Stimulates the production of new blood cells
- Increases healing rate
.jpg)
Patients and methods
Patients’ selection criteria
This is a retrospective study. It was carried out at the O.R.L Department, Ain Shams University Hospitals in the period between January 2011 and December 2014 with Institutional Review Board approval. Informed written consent was obtained from all participants. Forty-three patients (pts) were examined and treated for malignant otitis externa; they all had diabetes mellitus and were undergoing treatment to control diabetes mellitus. They were divided into two groups: group A (28 pts) only received the antibiotic ciprofloxacin and group B (15 pts) was treated with ciprofloxacin and HBO as an adjunctive treatment. The minimum follow-up duration in both groups was 2 months. Their ages ranged from 56 to 72 years. Both groups were similar in age, ear discharge bacteriology, and antimicrobial therapy.
Treatment strategy
Control of diabetes: All patients were treated with insulin injections and diabetes mellitus was strictly controlled. Ear discharge culture and sensitivity were assessed for all patients, which indicated growth of pseudomonas. Computed tomography (CT) scan of the temporal bone was performed before and 2 months after treatment. All patients were administered an antibiotic (ciprofloxacin). HBOT was administered at 2.0–2.5 ATA for 90 min per session. HBOT was administered for one session every other day for 2 months. HBOT was administered in the Naser National Institute in Sechrist hyperbaric oxygen chamber (Sechrist Monoplace Hyperbaric Chambers H-Series).
Comparison criteria
- Clinical microscopic examination (ear secretion, external canal edema, and granulation) was performed in all patients.
- Pain severity (the pain was noted for assessment of pain severity and degree of improvement and healing) - a pain score of 3 indicated severe pain, a pain score of 2 indicates moderate pain (sometimes controlled with strong painkillers), a pain score of 1 indicates mild pain (bearable without painkillers) and a score of 0 was specific to patients without pain
- Post-treatment CT scan: temporal bone was evaluated 2 months after initiation of therapy.
.jpg) | 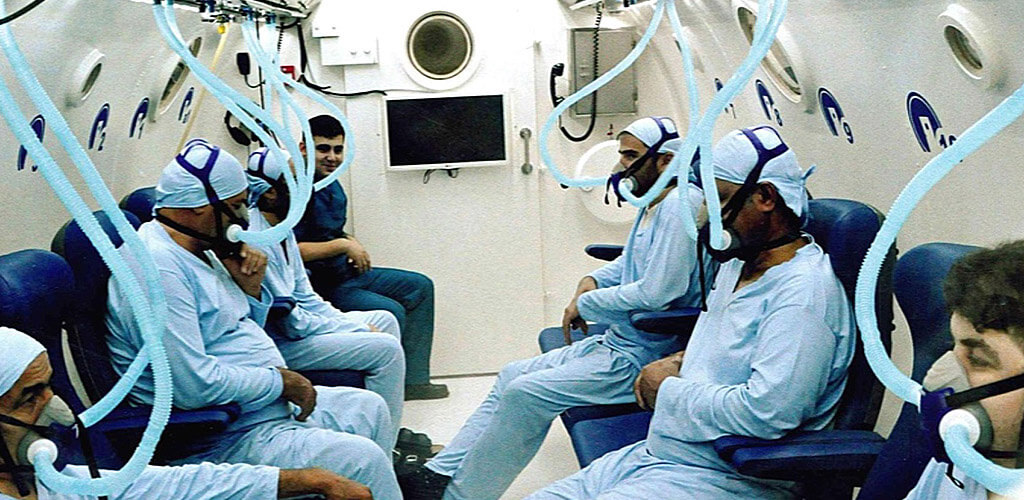 |
Results
A total of 43 patients had malignant otitis externa; these patients were divided into two groups: group A (n = 28) received only antibiotics (18 men, 10 women; mean age 64 years) and group B (n = 15) received HBO (90 min at 2, 5 ATA) in addition to antibiotics (10 men, five women; average age 62 years).
A total of 43 patients were identified, including 15 patients who received HBOT with antibiotics. The degree of improvement in patients' condition after treatment with adjuvant HBOT with antibiotics was elevated both symptomatically and clinically, as well as on CT scan of the temporal bone.
Discussion
Necrotizing invasive pseudomonas infection of the external auditory canal (malignant otitis externa) is an unusual but major condition in the elderly. The high morbidity, and even mortality, of this disorder, has been reduced by the early and intense use of combined antipseudomonal antibiotics. However, in patients with severe immunocompromise or infections involving the base of the skull, multiple cranial nerves, or meninges, conventional therapy is prolonged, intense, and relatively ineffective.
Infections for which HBOT has been studied and recommended by the Undersea & Hyperbaric Society of Medicine include necrotizing fasciitis, gas gangrene, chronic refractory osteomyelitis (including malignant otitis externa), mucormycosis, intracranial abscesses, and diabetic foot ulcers that have infections. In all of these processes, HBOT is used as an adjunct with antimicrobial agents and aggressive surgical debridement.
Radiologically, CT scans of the temporal bone indicated a considerable improvement with HBOT treatment, with less infection, opacity, fluid in the mastoid, and osteomyelitis changes. Overall, all cases treated with antibiotics and HBOT showed considerable subjective and objective improvement through examination and radiology, with more than 93% of cases cured and discharged early from the hospital. In contrast, those treated with antibiotics showed a slow improvement, a low percentage of complete healing (below 30%), persistent secretion and a certain degree of pain, and a longer duration of hospitalization. No complications have been reported with this treatment.
.jpg)
Davis and colleagues reported that all 16 patients responded promptly when 30-day HBO treatment was added to the antibiotic regimen, and all patients were retained for 1 to 4 years of follow-up. No complications were observed. Pilgramm and co-workers also showed that hyperbaric oxygenation had a positive influence on the reduction of P. aeruginosa in the external auditory canal and on pain symptoms.
Tisch and colleagues found, over more than 5 years, that 16 out of 22 patients treated on a multimodal concept did not relapse. Narozny and colleagues confirmed the role of HBO as a valuable, beneficial, and supportive classic treatment method in the treatment of malignant otitis externa caused by bacteria. Shupak and colleagues treated two patients with necrotizing otitis externa by hyperbaric oxygenation, followed by complete resolution without recurrence.
In the study by Saxby and colleagues, 70% of patients were considered cured and the condition did not recur on monitoring. HBOT confers minimal morbidity, but its role in malignant otitis externa (MOE) remains uncertain. The high mortality of MOE despite a maximum therapeutic intervention highlights the need for more effective treatment protocols.
Conclusion
The addition of HBOT to medical treatment is highly effective and has led to marked improvements in patient's conditions and the time required to achieve control of infection in these patients.
About Centrokinetic
Centrokinetic clinic offers all services necessary for a complete rehabilitation process, from the first consultation to the medical specialist to establish the correct diagnosis, to treatment and recovery.
Centrokinetic is the place where you will find clear answers and solutions for your motricity problems. The clinic is dedicated to osteoarticular conditions and is divided into the following departments:
- Orthopedics, a department composed of an extremely experienced team of orthopedic doctors, led by Dr. Andrei Ioan Bogdan, primary care physician in orthopedics-traumatology, with surgical activity at Medlife Orthopedic Hospital, specialized in sports traumatology and ankle and foot surgery.
- Pediatric orthopedics, where children's sports conditions are treated (ligament and meniscus injuries), spinal deformities (scoliosis, kyphosis, hyperlordosis) and those of the feet (hallux valgus, hallux rigidus, equine larynx, flat valgus, hollow foot).
- Neurology, which has an ultra-performing department, where consultations, electroencephalograms (EEG) and electromyography (EMG) are performed.
- Medical recovery for adults and children, department specialized in the recovery of performance athletes, in spinal disorders, in the recovery of children with neurological and traumatic diseases. Our experience is extremely rich, treating over 5000 performance athletes.
- Medical imaging, the clinic being equipped with ultrasound and MRI, high-performance devices dedicated to musculoskeletal disorders, and complemented by an experienced team of radiologists: Dr. Sorin Ghiea and Dr. Cosmin Pantu, specialized in musculoskeletal imaging.
Find the latest news by following the Facebook, Instagram and YouTube accounts of the Centrokinetic clinic.
Oxygen therapy in diving accidents
Diving accidents are accidents that can occur during diving, being specific to this activity, and are always an emergency. Learn the benefits of hyperbaric therapy and why it is useful in diving accidents.
READ MOREContraindications Of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has multiple medical and anti-aging uses. Like any medical treatment, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has certain contraindications. Find out here what are the contraindications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
READ MOREThe Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Reversing the Aging Process in Humans
Scientists in Israel say they can reverse the aging process. The key to this success seems to be hyperbaric oxygen therapy – breathing pure oxygen while sitting in a pressurized chamber for a certain amount of time. In this case, it's 90 minutes/session, with a frequency of 5 sessions per week, for 3 months.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in intestinal pneumatosis
Cystoid or cystic intestinal pneumatosis (intestinal emphysema) is a symptom that can occur in many gastrointestinal diseases. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be a successful treatment of cystoid intestinal pneumatosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in cell damage caused by radiation in gynecological cancers
Gynecological cancers treated with a combination of external beam radiation and brachytherapy, especially cervical and vaginal cancers, can result in the apex of the vagina receiving a high dose of radiation. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has positive effects on the radiated tissues, especially the head, neck, anus, and rectum.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in post-radiotherapy CNS injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves the use of so-called levels of oxygen under pressure to increase the level of oxygen in the blood. The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy involves oxygen treatment for soft tissue radionecrosis. Read this article and find out more.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygenation vs normobaric oxygenation in CO poisoning
Prolonged CO exposure is responsible for more than half of fatal poisonings and is also one of the leading causes of poisoning in Western countries. We aimed to compare the effectiveness of therapy with hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) versus normobaric oxygen (NBO) in the setting of carbon monoxide poisoning (COP).
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in diabetic foot
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be effective for Wagner's grade 3 and 4 diabetic foot ulcers and need to study the real problems with patients seeking treatment and demonstrates the need to study the real problems with patients seeking treatment. The results show that it is important to follow the treatment in order for the HBOT to be efficient.
READ MOREThe role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in sports medicine
Hyperbaric oxygen is used in sports medicine to reduce hypoxia and edema and is also effective in treating stroke injuries and acute traumatic peripheral ischemia. When used clinically, hyperbaric oxygen should be considered as an adjuvant therapy used as early as possible after the diagnosis of the lesions.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in muscle injuries
Muscle stretches are the most common muscle injuries suffered during performance sports. Rapid recovery from muscle injury is crucial for elite athletes who regularly are exposed to training and increased competition. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a safe and effective method, being a non-invasive treatment
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in sports injuries
Hyperbaric therapies are methods used to treat disease or injury using pressures higher than the local atmospheric pressure inside a hyperbaric chamber. The long-term effects are neovascularization (angiogenesis in hypoxic soft tissues), osteoneogenesis, and stimulation of collagen production by fibroblasts. This is beneficial for wound healing and recovery after irradiation.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in proctitis generated by radiation
Proctitis is the inflammation of the rectal mucosa causing pain, discharge, and other unusual symptoms. Pain can occur during bowel movements, it can be acute or chronic. Symptoms may vary, but the most common is tenesmus (the feeling of needing to go to the toilet), a sensation that persists even after using the toilet. This treatment should be offered to patients who fail to recover with conventional treatments for radiation-induced proctitis.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in refractory osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone or marrow caused by bacteria or mycobacteria. Hyperbaric oxygen treatments can be considered an American Heart Association (AHA) Class II recommendation for the treatment of chronic, refractory osteomyelitis
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in tinnitus
Hyperbaric oxygenation allows a controlled increase in oxygen pressure in the blood. This technique can be used in cases of tinnitus and sudden deafness, when certain changes in the inner ear and brain generate a lack of oxygen and, therefore, a limited intake of energy.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy of ischemia and reperfusion injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been found to ameliorate the damaging effects of reperfusion by early modulation of inflammation, maintenance of metabolic function in downstream tissues, and reintroduction of oxidation scavengers.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in the treatment of second degree burns
HBOT has a beneficial effect on burn wound healing by reducing edema and ensuring there is adequate oxygen in microcirculation. It may speed up epithelialization and suppress unnecessary inflammation that could negatively affect normal wound healing. With further research, HBOT may become an adjuvant therapy to surgery.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric therapy is a form of medical treatment that involves exposing the body to pure oxygen at a higher pressure than normal. There are about 45 diseases approved worldwide to be treated with hyperbaric oxygen.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in the management of patients with malignant otitis externa
Malignant otitis externa is a rapidly spreading bacterial infection that is aggressive and may be fatal if left untreated. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment in which the entire body is placed in an airtight chamber at increased atmospheric pressure and has been proven to be effective for several different medical conditions.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute myocardial infarction
If left untreated, MI will lead to the progressive loss of viable cardiomyocytes, impaired heart function, and congestive heart failure. Oxygen cycling therapy serves as a very attractive option for the treatment of myocardial infarction, because it offers some of the greatest benefits while reducing treatment time and inconvenience to the subject.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen in ischemic ulcers
The present study has demonstrated that adjunct HBOT enhances the reduction of ulcer area and depth at 4 weeks in T2DM patients with ischaemic DFUs. HBOT is known to ensure hyperoxygenation of ischaemic tissue and restoration from hypoxia. Discover the hyperbaric medicine center open in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in femoral condylar osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis of the knee (ONK) is a form of aseptic necrosis resulting from ischemia to subchondral bone tissue. Typically, treatment is invasive. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may provide a noninvasive alternative by improving oxygenation and reperfusion of ischemic areas. This study evaluates the efficacy of HBOT in a series of ONK patients.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in femoral head necrosis
Femoral head necrosis (FHN), also called avascular necrosis, or femoral head osteonecrosis is a common multifactorial condition that affects patients of any age and can lead to substantial clinical morbidity. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) is one of the proposed treatments. Indeed, tissue oxygen promotes angiogenesis that reduces edema. Read about the effectiveness of this treatment.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a devastating and common eye condition. It presents a sudden, unilateral, and painless loss of vision. Even when treated promptly, an acute obstruction of the central retinal artery usually leads to severe and permanent loss of vision.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in irradiated maxillofacial dental implant
There are numerous studies reported for the effectiveness of HBO in the treatment of osteoradionecrosis of various bone tissues. In addition to its usefulness in treating osteoradionecrosis, this therapy can prevent it. It also combats the negative effect of irradiation, stimulates osseointegration, and improves the survival rate of the implant.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in hear loss
The auditory function in the inner ear is maintained by the cochlea, which is known to have a high oxygen demand. Hyperbaric oxygen can increase the tension of oxygen in the perilymph and restore hearing in a significant number of patients with sudden hearing loss. Patients can be treated in a single-seater hyperbaric chamber or in a multiplace chamber.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in traumatic ischemia
Limb trauma, which leads to direct tissue damage, plus local hypoxic disorders caused by the resulting edema, causes acute peripheral ischemia. Surgical treatment and hyperbaric oxygen are not concurrent treatment modalities but are best used to complement each other in order to provide the best outcome for the patient.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in venous embolism
Small gas embolisms, as in this case, present serious risks, especially the complication of cerebral air embolism. To prevent neurological complications, it is necessary to urgently remove the air bubble. HBOT reduces the volume of the bubble, helps eliminate nitrogen, and improves the oxygenation of potentially hypoxic tissue. See the results of hyperbaric therapy in venous embolism.
READ MOREHyperbaric therapy in osteoradionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a common consequence of radiation provided to cancer patients. Currently, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has a major role in improving wound healing in patients with ORN.
READ MOREHyperbaric oxygen therapy in soft tissue radionecrosis
Discover the hyperbaric medicine center open in our clinic. Centrokinetic has the top-performing hyperbaric chamber in Bucharest, with multiple medical and anti-aging uses. The Baroks chamber has 5 seats, and operates at a constant pressure of 2.5 atmospheres, being fully automated and having protocols for each condition, and can be used individually for each patient.
READ MORESUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT