.jpg)
For all traumatic or chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the Centrokinetic private clinic in Bucharest is prepared with an integrated Orthopedic Department, which offers all the necessary services to the patient, from diagnosis to complete recovery.
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery of Centrokinetic is dedicated to providing excellent patient care and exceptional education for young physicians in the fields of orthopedic surgery and musculoskeletal medicine.
Centrokinetic attaches great importance to the entire medical act: investigations necessary for correct diagnosis (ultrasound, MRI), surgery, and postoperative recovery.
Discover the open MRI imaging center in our clinic. Centrokinetic has a state-of-the-art MRI machine, dedicated to musculoskeletal conditions, in the upper and lower limbs. The MRI machine is open so that people suffering from claustrophobia can do this investigation. The examination duration is, on average, 20 minutes.
Clinical, experimental, and biomechanical studies have shown that the menisci are integral, vital components of the knee. The future of the knee depends on its integrity. Therefore, our medical team approaches each case with the idea of saving as much of the affected meniscus as possible. It is very important to understand that not all meniscus lesions have a surgical indication, but at the same time, certain lesions require an emergency approach, with surgery as soon as possible.
.jpg) | .jpg) | .jpg) |
The surgery is arthroscopic, practically a minimal surgical procedure with a one-day hospitalization, minimal incisions, pain, and almost non-existent complications. Arthroscopy is preceded by clinical and paraclinical investigations (MRI, CT, X-ray) that provide the doctor with a preoperative diagnosis. During this arthroscopy, our team inspects the entire joint, namely the cruciate ligaments, both menisci, quantifies the bone ratios and the condition of the articular cartilage. If during the operation we see other lesions, they can be solved with arthroscopy.
.jpg) | .jpg) |
Meniscal injuries are of several types:
- Longitudinal
- Bucket handle tear
- Bucket handle tear with displacement
- Posterior horn bone detachments
- Horizontally
- Radial
- Degenerative
- In the parrot's beak
.jpg)
The operation lasts about 20-40 minutes, under spinal or general anesthesia. The anesthetist discusses with the patient, during the pre-anesthesia consultation, to evaluate the general state of health. Usually, the pre-anesthetic consultation is performed in the week before the surgery, when the patient's blood tests are also collected.
.jpg) | .jpg) |
.jpg) | .jpg) |
.jpg) | .jpg) |
The intervention involves making 2 minimum incisions (2-3 mm) on either side of the patellar tendon, through which are introduced: the camera and the necessary instruments. The images captured by the camera are viewed by the medical team and the patient on a screen. After the intervention, the patient is brought to the salon, and within 12 hours he can mobilize. In the next period, the foot should be kept up on a pillow, and an ice pack should be applied for 3-4 days. Postoperative treatment consists of antibiotic therapy, analgesics as needed, anti-inflammatory. The dressing is changed every 48 hours, and the threads are removed every 14 days.
Arthroscopic surgery of meniscal lesions involves:
Meniscectomy: This is a controversial topic. Meniscectomy addresses rupture that cannot be repaired or that repair does not restore meniscal function.
The meniscus is vascularized in the middle, and avascularized to the periphery, so all lesions located in the avascularized area of the meniscus are indicated for meniscectomy.
The type of meniscectomy performed depends on the rupture and varies from partial to subtotal and total, but the latter is rarely indicated. Any meniscectomy is performed with maximum parsimony, knowing the particularly important functions of the meniscus and the late consequences of its excision (osteoarthritis of the knee). It will be preferable, whenever possible, the partial circumferential meniscectomy, which preserves the peripheral edge of the meniscus and with it the functions of transmission and taking over the load. The results of partial meniscectomy are far superior to the results of subtotal or total meniscectomies.
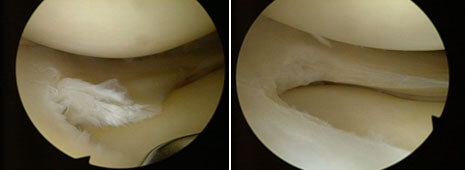
Partial meniscectomy is of 2 types:
- segmental, in which the excised part involves the entire width of the meniscus in a certain sector, so also a part of the peripheral edge
- circumferential, in which the excised part comprises, on a certain length, the central portion of the meniscus, without affecting its periphery. It is the most common form of meniscectomy.
Our medical team has given up sectoral meniscetomies, preferring to suture the meniscus in these cases to avoid the harmful consequences of a sectoral meniscectomy.
.jpg) | .jpg) | .jpg) |
The meniscus injury is not a surgical emergency unless the knee is blocked (cannot be flexed or extended). However, a neglected meniscus injury will determine, in addition to the characteristic symptoms (pain, partial functional impotence, hydrarthrosis), a process of fibrillation and fragmentation of the articular cartilage, practically leading in time to the installation of an irreversible arthritic process. The installation of the arthritic process cannot be quantified in time, it can appear sometimes after 1 year, sometimes after 4-5 years, and depends on: the type of meniscal lesion, the patient's weight, physical activity.
The recovery period after meniscectomy is 6-8 weeks, during which time the patient will follow a physical therapy program. A performance athlete will resume training after 4 weeks.
The meniscus suture is the ideal solution in the treatment of meniscus injury.
Unfortunately, not every meniscus injury is suturable, and the healing rate is 86% if the suture is done in the first month after the trauma. However, all percentages of healing in studies over the past two decades have improved with the combination of regenerative treatments in meniscal sutures.
Currently, it is accepted that longitudinal, vertical lesions located in the peripheral 1/3 of the meniscus with a length greater than 1 cm can and must be repaired. If there is both a repairable and an irreparable lesion, we can suture the first lesion and resect the second. These 2 types of injury occur especially in an attempt to brutally unlock a locked knee.
The surgery involves making two incisions in the anterior part of the knee, sometimes associating another one or two incisions in the medial area of the joint. The interaction lasts 24 hours, and the anesthesia is spinal or general.
There are several methods of suturing the meniscus:
- inside-out: in which the sutures are directed from the inside of the knee to the periphery
- outside-in: it is easy for ruptures in the anterior 2/3 of the meniscus and difficult for posterior ruptures
- all inside: addresses only the ruptures of the posterior 1/3
.jpg) | .jpg) | .jpg) |
After the surgery, a special orthosis is mounted on the leg, the patient having to use it for 6 weeks. The recovery period is much longer compared to recovery after meniscectomy and lasts on average 6 months.
Very often meniscal lesions are associated with ruptures of ACL or PCL, MCL lesions, or articular cartilage lesions. In these situations, preoperative, imaging (MRI) and clinical diagnosis are very important, so that the medical team is prepared to solve all the problems in a single surgical stage.
Bone reinsertion of the meniscal posterior horn: in 7-10% of the situations in which we meet a patient with LIA rupture, we can observe at the clinical examination a very high instability (there is a test, Pivot shift grade III). This instability often hides a disinsertion of the posterior horn of the external meniscus, on the bony surface of the tibial plateau. Lack of preoperative (MRI) or intraoperative diagnosis of the lesion will lead in time to ligamentoplasty failure.
Bone reinsertion of the meniscal horn is a complex intervention and involves performing one or two bone channels with a special guide, passing wires or strips through the meniscus, then through the bone channels and distal fixation to the bone surface of the wires.
The intervention has a one-day hospitalization, which involves making two incisions in the anterior part of the knee, sometimes associating another incision of about 1.5 cm in the lower part of the knee joint, under spinal or general anesthesia. The recovery protocol starts the next day and lasts 6 months.
Following any surgery, medical recovery plays an essential role in the social, professional, and family reintegration of the patient. Because we pursue the optimal outcome for each patient entering the clinic, recovery medicine from Centrokinetic is based on a team of experienced physicians and physical therapists and standardized medical protocols.

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT




































































































































