For all traumatic or chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the Centrokinetic private clinic in Bucharest is prepared with an integrated Orthopedic Department, which offers all the necessary services to the patient, from diagnosis to complete recovery.
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery of Centrokinetic is dedicated to providing excellent patient care and exceptional education for young physicians in the fields of orthopedic surgery and musculoskeletal medicine.
Centrokinetic attaches great importance to the entire medical act: investigations necessary for correct diagnosis (ultrasound, MRI), surgery, and postoperative recovery.
Discover the open MRI imaging center in our clinic. Centrokinetic has a state-of-the-art MRI machine, dedicated to musculoskeletal conditions, in the upper and lower limbs. The MRI machine is open so that people suffering from claustrophobia can do this investigation. The examination duration is, on average, 20 minutes.
The brachial biceps muscle originates through the short head, at the level of the coracoid process of the scapula, and through the long head, on the supraglenoid tubercle. The insertion is made on the radial tuberosity and with the help of the bicipital aponeurosis, in the deep fascia on the medial part of the forearm.
The brachial biceps muscle crosses both the shoulder joint and the elbow joint and is responsible for elbow flexion and forearm supination.
Distal rupture of the brachial biceps muscle usually occurs in middle-aged men, when lifting a heavy weight, with the elbow flexed at 90 degrees or when the biceps contracts at unexpectedly high resistance, in discordance with the patient's training degree. The complete rupture is easy to diagnose, the muscle being ascended, and the flexion and extension movement of the elbow being painful. Lack of forearm supination is a clear sign of tendon or muscle rupture. To elucidate the diagnosis, our medical team recommends an MRI examination of the elbow. The treatment of choice is surgery.
.png)
Surgical technique
Under locoregional (axillary or latero-cervical block) or general anesthesia, an incision of about 7-8 cm is made in the anterior part of the elbow in the shape of the letter "S". A careful dissection is performed to discover the vascular-nervous structures of the subcutaneous tissue (lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve and cephalic vein).
After this thorough dissection, the tendon abutment is identified, and it must be mobilized and released from the scar tissue or surrounding adhesions. In chronic cases, extensive dissection may be required.
.png)
After identifying and mobilizing the tendon abutment, attention should be directed to the place of insertion on the radial tuberosity. In general, dissection to radial tuberosity can be easily performed with a finger or other blunt tool. Using Hohman retractors, the place of insertion of the muscle on the radial tuberosity is highlighted.
.png)
Subsequently, we make sure that it is possible to reinsert the tendon in terms of tendon length or retraction. In chronic cases, there may be muscle retraction. If the tendon reaches radial tuberosity at 30 elbow flexion, then reinsertion is possible without extensive muscle dissections. If not, additional mobilization may be required. If the tendon does not reach radial tuberosity, despite extensive dissection, it is necessary to use a ligament autograft to obtain the desired muscle length. Our medical team uses the quadriceps muscle.
At the level of the radial tuberosity, a guide brooch is inserted, subsequently making a channel with a 3.2mm, unicortical drill. The tendon abutment is fixed with the help of a special implant, called TightRope, and super stabilized with a bioinert anchor (it does not interact with the surrounding tissues).
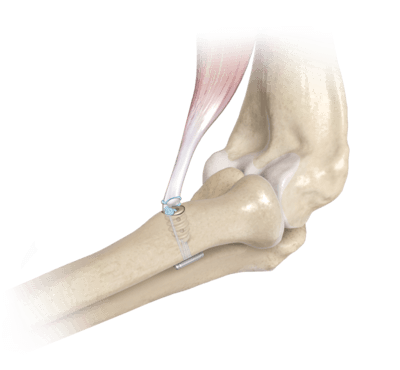
Post surgery
After the operation, the patient remains hospitalized for 1 day. He will receive pain medication and antibiotics during his hospitalization. The operated limb is immobilized in a mobile elbow orthosis, the patient is advised not to make elbow movements, from the first postoperative day, except the fist and fingers.
Patients will wear a compressive bandage at the elbow for 5 days and will use a special hinged orthosis, which can be easily removed for personal hygiene. Patients can return to family and professional activities quickly, up to 6-8 weeks.
.png)
At home
Although recovery after this operation is much faster than classic intervention, it will still take a few weeks for you to fully recover. You should expect pain and discomfort for at least a week postoperatively.
You must be careful not to force the operated area by making very wide flexion and extension movements in the first weeks because the pain and discomfort can worsen. You can take a bath, but without wetting the bandage and incisions. The threads are suppressed at 14 days postoperatively.
At 6 weeks postoperatively, an x-ray is necessary to see how the affected joint heals. Driving is allowed after 6 weeks, and hard physical work after 12-16 weeks.
Physical therapy plays a very important role in the rehabilitation program, and the exercises must be followed by a physical therapist until the recovery period ends.
It is very important to follow the recovery program strictly and seriously for the surgery to be a success. Our medical team works, on average, 18-24 weeks with the patient until the complete recovery of the operated area. Following any surgery, medical recovery plays an essential role in the social, professional, and family reintegration of the patient. Because we pursue the optimal outcome for each patient entering the clinic, recovery medicine from Centrokinetic is based on a team of experienced physicians and physical therapists and standardized medical protocols.

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT





































































































































