See details
READ MORE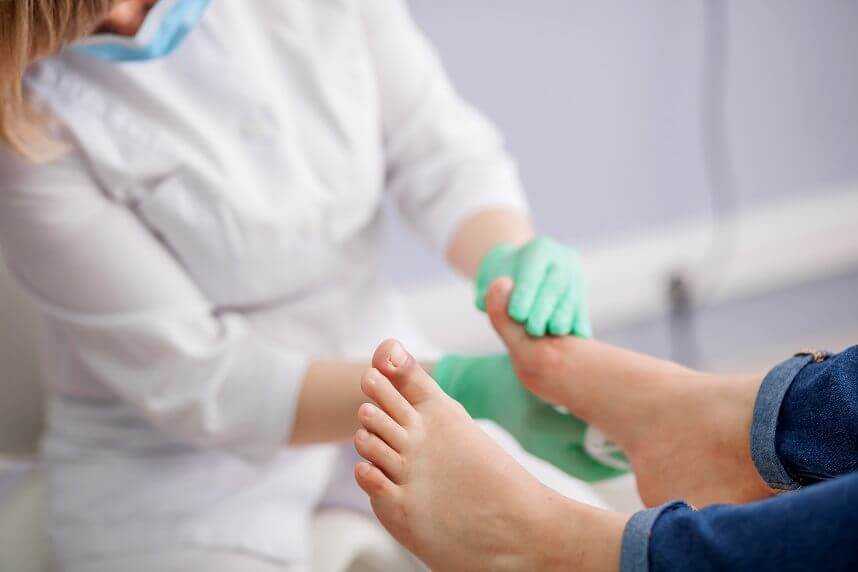
Debridement of the diabetic foot
Centrokinetic has a dedicated vascular surgery department, coordinated by Mrs. Dr. Neagu Cristina, primary doctor of vascular surgery, specialized in diagnosis and treatment of blood diseases in arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels.
Diabetic foot is a complication of diabetes and can include: ulceration, infection and osteoarthropathy. Come to Centrokinetic for debridement of the diabetic foot (Charcot's foot).
The two main problems facing the patient with diabetes are poor circulation and impaired endings nervous. These can lead to the appearance of blisters and skin lesions that, untreated, can become infected and lead to serious problems ranging from extreme cases to amputations of the toes or feet.
Therefore, proper prevention and care of the feet are essential for early identification of problems and diminishing the consequences.
The complications of long-term diabetes are vascular and neurological, therefore, the diabetic foot syndrome represents one of the worst consequences from the point of view of the health complications it generates and the impact on the quality of life.
Diabetic foot refers to all the changes produced of diabetes in the foot. In the most advanced phases it can lead to diabetic gangrene, most commonly located at the level of one or more fingers and which can extend to the entire leg.
The rules of hygiene and care for prevention must strictly observed, and the diagnosis in the early stages of possible injuries and the establishment of adequate treatment yet from the first signs of ulcer can avoid amputation, total or partial, of the affected limb.
Diabetic foot ulceration
Diabetic foot ulcer is one of the major complications of diabetes, occurs in 10-15% of patients with diabetes and precedes 80% of the distal amputations of the foot.
Wound healing is a natural tissue phenomenon destroyed. Diabetic patients, however, have metabolic disorders, which prevents certain stages in this healing process, through persistence of an inflammatory phase in wounds, culminating with delayed healing.
The most common component of the diabetic foot is ulceration. Ulceration is a painful wound that does not heal: the skin no longer covers that area and the tissues are exposed from the depths. Ulcerations occur frequently as a result of small cuts, blisters or burns.
Diabetic patients are also prone to neuropathy, which occur as a result of high blood sugar levels on a long period of time.
Chronic neuropathy
May cause dry skin, which further leads to the appearance cracks and calluses (corns). When the skin is damaged, the natural barrier to bacteria also disappears and can reach the subcutaneous tissue which can cause infections.
Neuropathy also leads to loss of sensitivity foot and as a result, we no longer feel pain when a basic or callus, because the area is numb. Because we don't feel nothing, we continue to walk, we continue to aggravate the problems and to favor the appearance of complications, the infection of the lesions being the most frecvent between them.
Neuropathic osteoarthropathy
Another complication of diabetes is neuropathic osteoarthropathy which occurs due to damage to the nerve endings of the feet. This is also called the Charcot leg, after French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot. In patients with severe neurological impairment, the evolution can be severe, toward weight loss of the leg bones, microfractures and even sagging joints. As a result, the foot may deform.
Diabetic foot care
Due to decreased or lack of sensitivity, often patients are late to seek medical advice, which leads to complicating a seemingly trivial injury. That is why it is necessary that a person with diabetes to give daily attention for footwork proper care to avoid complications that, in certain situations, can be serious.
- Observation of the condition of the feet should be done daily to identify, in the early stages, any change. Carefully checking of the hardest to reach areas and those between fingers (you can use a mirror or the help of a member of family);
- The feet should be washed daily with warm soapy water and carefully wiped (especially in interdigital spaces);
- Do not put the wet foot in the socks, because the moisture predisposes to fungal infections;
- Cut your nails straight. The corners should be rounded to avoid possible injuries accidental;
- A moisturizer is applied to the well-dried skin of the foot to avoid drying out the foot, which can lead to cracks and these, further, to the appearance of infections bacterial (cream does not apply in interdigital spaces);
- Shoes should be comfortable, not tight;
- A person with diabetes should not walk barefoot. Of it is also not recommended to put the bare foot in the shoe.
- You should use 100% cotton socks, because they do not maintain moisture. Stockings should be changed several times a day, if the foot sweats;
- People with diabetes may have decreased sensitivity (or even absence), must be very careful of cold or water warm because they may not feel the temperature properly and they can get hurt.
Any symptoms or signs of a change in the feet, lack or low sensitivity, itching, cracking, flaking with irritation, blackening of the nails, it can be an alarm signal, so the diabetic patient must go to the doctor.
Prevention is the best method of treatment for the diabetic foot. Preventive strategies combined the education fo the patient with prophylactic skin and nail care and appropriate footwear.
SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT