Article written by: ,
Actualizat: 16-01-2024 / Publicat: 25-01-2017

Shoulder rehabilitation
The shoulder is composed of several anatomical entities, among which we mention: the shoulder articulation, the acromio-clavicular articulation, the rotator cuff, the deltoid muscle, the biceps brachii muscle, these formations being frequently exposed to injuries.
These injuries can be direct (falling on the shoulder, blows) or indirect (falling on the hand or elbow).
The loss of the normal ratio between the bones of the shoulder articulation (scapula and humerus) is called scapulohumeral dislocation. This can occur following an indirect trauma, by falling on the hand with the elbow extended. It represents a medical emergency due to the pains and complications that it develops and it is reduced orthopedically, immediately after the presentation in the emergency room, after a preliminary radiological evaluation. In case of impossibility of reduction, this will be performed under general or surgical anesthesia. In 48% of cases, the dislocation is accompanied by recurrences, this percentage varying according to age. Thus, we are talking about recurrent shoulder dislocation that can only be treated surgically (Latarjet / Bankart procedure).
Acromio-clavicular disjunction occurs as a result of a direct trauma, by falling on the shoulder. By breaking the ligaments of this joint, the upper limb is lowered by gravitational force, appearing a step at the junction of the scapula with the clavicle. The treatment is conservative (immobilization and rest) for mild disjunctions (grade I and II), the surgical treatment being reserved for severe disjunctions (grade III, IV, V) and for performance athletes.
Scapula snapping syndrome occurs when the movement of the scapulo-thoracic articulation describes a discomfort or sounds of scraping, grinding, cracking. The treatment is conservative and consists in the administration of analgesic / anti-inflammatory medication, local cold applications, physiotherapy, the surgical treatment being reserved for patients in whom the conservative treatment has failed.
A special entity is the rotating head (ms. Supraspinous, infraspinous, subscapular and small round) prone to ruptures or humeral disinsertions. It is found in the upper part of the shoulder joint, and is affected either by low but repeated injuries: handball, hammer throwers, bodybuilders, sport dancing, or by an indirect trauma, violent by falling on the hand or elbow with the arm next to the body. In this case it may be accompanied by a fracture of the small tubercle of the humeral head. The treatment is surgical and consists in the reinsertion of the hair with anchors.
Calcium tendonitis of the shoulder occurs by the deposition of calcium deposits in the muscle tendons that are found in the shoulder, especially in the supraspinatus muscle. Along with calcium deposits, a local inflammation will appear, accompanied by severe pain. It occurs especially in people over 40 years, the treatment consists of rest, analgesic / anti-inflammatory medication, cold local applications, followed by a period of physiotherapy. If the pain persists and the patient loses shoulder mobility, surgery is recommended.
The articular capsule, even if it is thickened in the scapular part, is prone to lesions. SLAP injuries (disinsertions or ruptures in the upper part of the joint), anterior ruptures (in antero-inferior dislocations) or posterior lesions may occur. These lesions are treated surgically by reinserting the capsule with anchors or by sutures.
![]()
Adhesive capsule (frozen shoulder) occurs especially in the 5th and 6th decade of life, being more common in females. It is characterized by limiting the mobility of the shoulder by contraction and post-traumatic scarring of the joint capsule. Causes can be multifactorial: direct trauma to the shoulder, cervical syndromes, autoimmune processes. The symptoms consist of moderate pain in the shoulder, which is accentuated at night, with stiffness and progressive limitation of movements. Over time, the patient will no longer have pain but active and passive shoulder mobility will be severely limited. The treatment of choice is non-surgical and consists of intra-articular injections with corticosteroids and analgesic / anti-inflammatory medication. If the symptoms do not subside, surgery is recommended (articulation distension under arthroscopic control, mobilization under anesthesia, synovectomy or even arthrolysis).
Rupture of the proximal tendon of the brachial biceps muscle occurs when lifting a weight equal to or greater than 68 kg (represents the tension force at the tendon). The rupture is located at the level of the intra-articular portion or in the proximal part of the intertubercular groove. Most injuries, except for young people, are treated conservatively, the only drawback being the aesthetic, mobility and strength being maintained in the upper limb.
Brachial biceps muscle tendonitis is usually associated with other primary shoulder conditions: impingement syndrome, intertubercular canal stenosis, rotator cuff injuries. The reference point in the patient's anamnesis is a pain in the anterior part of the shoulder, accentuated by the anteflexion movements of the arm and the internal rotation of the arm over 10 degrees. Treatment can be conservative (NSAIDs, local cortico-therapy, locally infiltrated anesthesia, physiotherapy) or surgical (tenotomy or tenodesis).
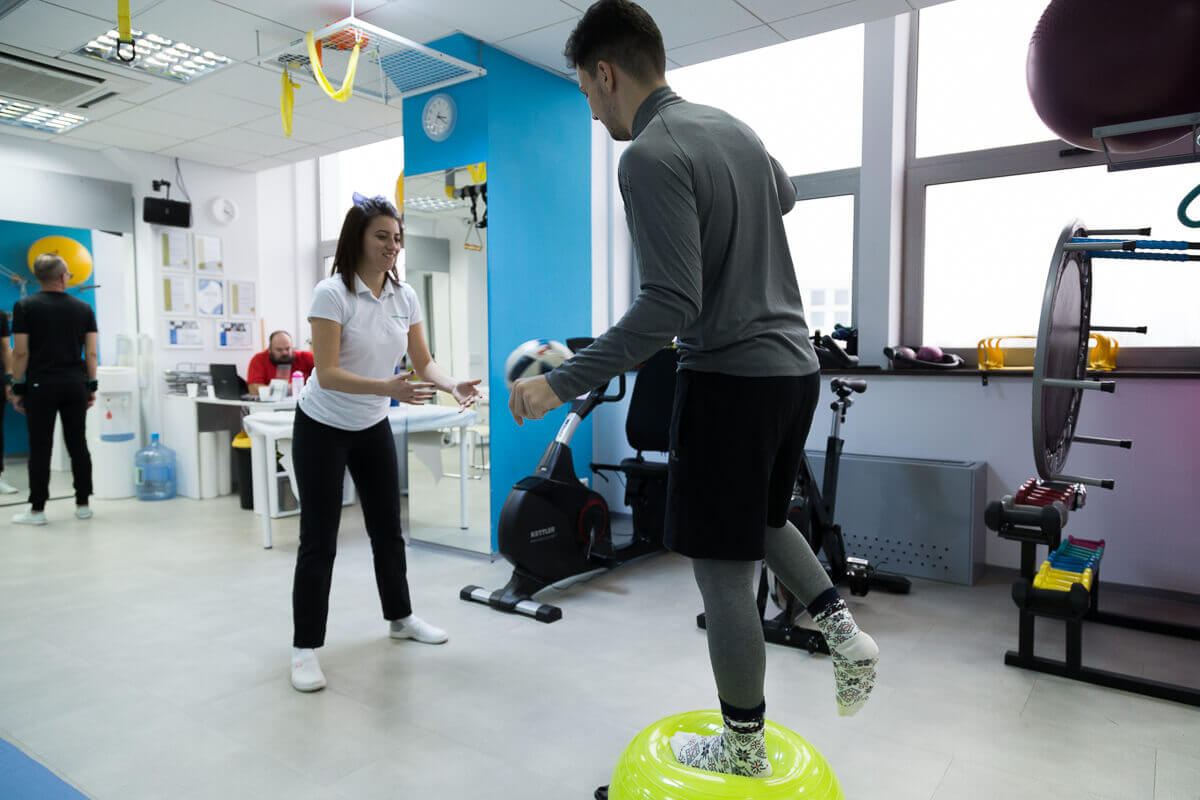
The shoulder is a complex joint, exposed to direct and indirect trauma, and sports pathology in the shoulder is very varied and misleading. Most of the time the diagnosis requires multiple paraclinical investigations. The treatment indicated by the orthopedist, even if it is conservative with local or oral anti-inflammatory drugs, immobilizations, physical rest, ice, local infiltrations, must be accompanied by a complex medical recovery program in order to obtain a good functional result. Most of the time, at the end of the orthopedic treatment, the patient has a deficit of mobility, vascularity disorders, sensitivity, muscle atrophy, that's why Dr. Andrei Ioan Bogdan will recommend a complex recovery program that consists of physiokinetotherapy.
Physiotherapy has the role of decreasing inflammation and is recommended from the first symptoms of the condition to reduce pain, inflammation, practically to improve the general condition of the patient. It lasts on average 10 days, followed by an evaluation by the attending physician. Physiotherapy has the role of restoring function, mobility, muscle tone, ensuring the patient's integration into the family, social and professional environment.