See details
READ MORE
What is tendinitis?
Tendinitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of a tendon, which is a bridge between a bone and a muscle (insertion or origin), with which the muscle submits to mechanical action the joints with which it borders. Elasticity is a property of the tendon that decreases the risk of it rupturing in a context of violent muscle contracture. More precisely, the tendinitis is characterized by the partial rupture of some fibers belonging to the tendon associated with a local edema. These lesions can evolve over days, weeks or even months.
If you are experiencing an inflamed tendon and do not know the causes, find out in this article if your symptoms are associated with tendinitis.
Causes and prevention
Causes
The most often incriminated is the sports activity, through which the tendon is subjected to exaggerated and repeated demands that can lead to tendinitis. The most often incriminated is the sports activity, through which the tendon is subjected to exaggerated and repeated demands that can lead to tendinitis.
Direct injuries to the tendons are also a cause, especially in the Achilles / patellar tendons. Less common is tendinitis caused by a neighboring anatomical structure that rubs against the tendon: more specifically we are talking about the wide fascia (thigh fascia) which may have a conflicting relationship with one of the prominent femoral bones.
Among the general causes of tendinitis, we mention:
- obezitate
- obesity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- the cold;
- decreased joint mobility;
- no heating;
- inadequate footwear;
- insufficient hydration.
Prevention
Tendinitis can be prevented by a series of rules. First, this condition can be prevented by toning the muscles to reduce the strain on the tendons. If the patient feels pain in the area of the tendons, it is necessary for him to stop the activity or exercise that causes the pain.
It is important to avoid keeping the articulations in the same position for a long time. Probably the most common way to prevent tendinitis is to perform warm-up exercises before the patient starts doing any type of sport.

Tendonitis symptoms
Pain is the most common symptom, frequently found at rest, it intensifies when we palpate and when mobilizing the articulations neighboring to the inflamed tendon. The pain is acute, stinging, associated with inflammation of the surrounding area: the region is described as erythematous, swollen and hot. Then the decrease in muscle strength in the entire affected area (elbow, ankle, finger, knee, hand, shoulder) is described.
Tendinitis can evolve over several months. Tendinitis can heal spontaneously or can persist and become chronic. Tendon rupture is a complication of tendinitis (e.g., quadriceps / patellar tendon rupture), with a high severity, but is quite rare, manifested by pain of extreme intensity associated with total functional impotence. The most commonly affected are: plantar fascia (plantar fasciitis), quadriceps tendon (quadriceps tendinitis), Achilles tendon (Achilles tendinitis) and patellar tendon (patellar tendinitis).
Rarely, tendinitis can be found in the hamstrings. Belonging to the tendonitis of the knee, we mention the conflict syndrome of the wide fascia, being also known as the iliotibial band syndrome.
Diagnostic methods
In order to establish the diagnosis of tendinitis, we focus on: the clinical examination, the character and location of the pain, the possibility of triggering a live pain by palpation of the tendon and auxiliary paraclinical examinations: radiography of the affected area, ultrasonography (ultrasound) or MRI.
Centrokinetic, through the medical team, developed a very strict algorithm for diagnosing patients with tendon pain: initially all patients perform a clinical examination, then an ultrasound or osteo-articular MRI. Centrokinetic has one of the most efficient imaging departments in Bucharest, being equipped with a Samsung ultrasound and Esaote MRI, dedicated to osteo-articular diseases. Also, our radiologists are overspecialized in osteo-articular diseases.
Tendinitis treatment
The most important step in the treatment of tendinitis is to identify the cause and eliminate it. The initial phase of tendinitis treatment is to control inflammation. If the episode is acute (the tendon is painful to the touch and while walking, edematous), treatment should focus on reducing inflammation.
When we want to reduce inflammation in tendinitis, we will focus in the first phase on relaxing the tendon, physical exercise being prohibited. This is the key difference between treating a sprain and treating tendinitis. Early exercises can aggravate the pathology, the patient presenting an accentuation of the symptomatology, respectively of the edema, instead of its reduction. Also, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory medication, also in order to reduce the inflammatory process.

Physical therapy in the treatment of tendinitis
As the pain and edema dissipate, the patient can begin a series of physical therapy exercises to improve tendon mobility and strengthen it. However, due to the delicate nature of the tendon, these exercises must be performed with great care and under the close supervision of a physiotherapist so as not to deviate from the healing process.
Flexibility exercises should focus on the gradual elongation of the tendon without causing an increase in pain. If fibrosis or tendon adhesions are observed, several soft tissue techniques will be applied to release adhesions that may interfere with the tendon's ability to elongate.
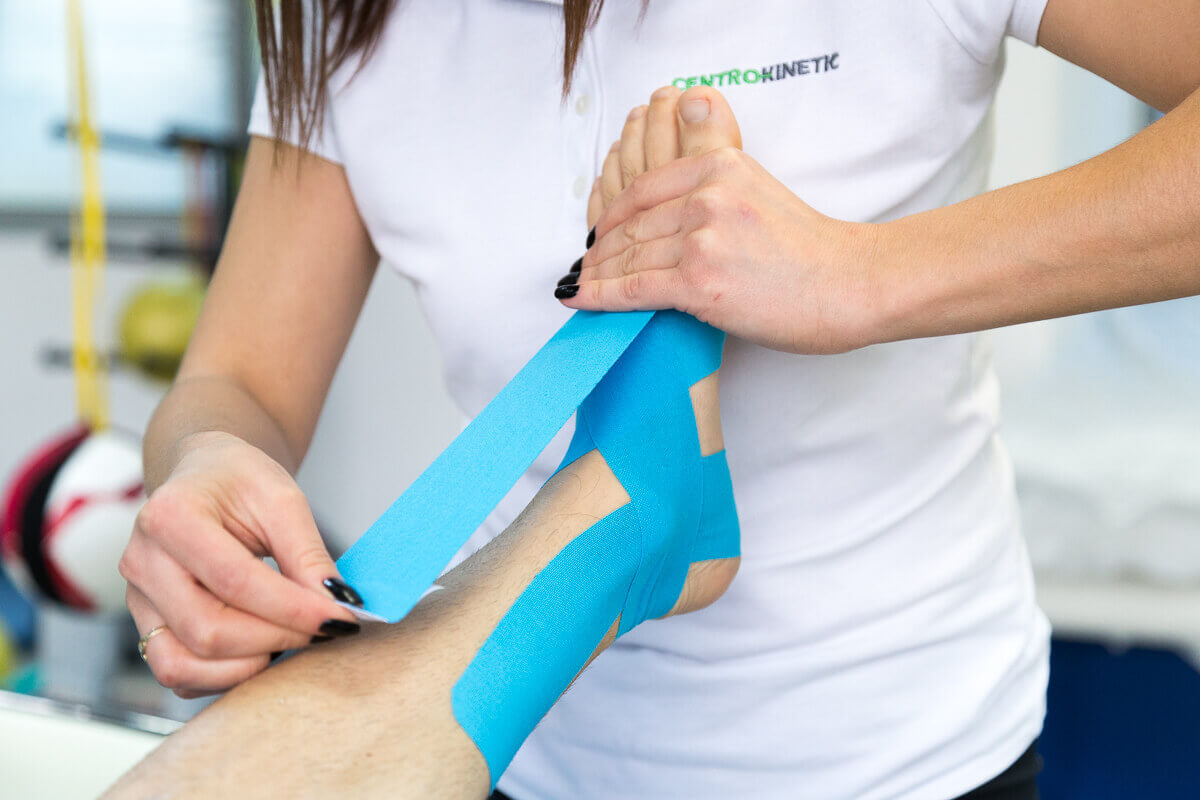
Strengthening exercises focus on low intensity exercises, performed in frequent repetitions so as not to exert too much stress on the tendon. Studies support performing eccentric exercises to strengthen the tendon because these eccentric exercises are less stressful on the tendon than other forms of strengthening exercises. When the patient performs eccentric exercises, they should be started with a shorter range of motion, so as not to put any additional stress on the tendon.
For example, when treating brachial biceps tendinitis, eccentric exercises should be started with the shoulder in a flexed position. The patient resists the physiotherapist's attempt to extend his arm, but the resistance is interrupted before full extension. As the patient's condition improves, he will advance from endurance and eccentric exercises to concentric exercises, which involve fewer repetitions and a progressive increase in endurance.
SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY STORIES

MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
CONTACT US
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
FOR AN EXAMINATION
See here how you can make an appointment and the location of our clinics.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT